----National Technical Guidelines for Animal Epidemic Immunization in 2022
In order to do a good job in immunization against animal epidemics, the China Animal Epidemic Prevention and Control Center specially formulated the National Technical Guidelines for Immunization against Animal Epidemics in 2022 in accordance with the requirements of the Guidelines for Compulsory Immunization of National Animal Epidemics (2022-2025).
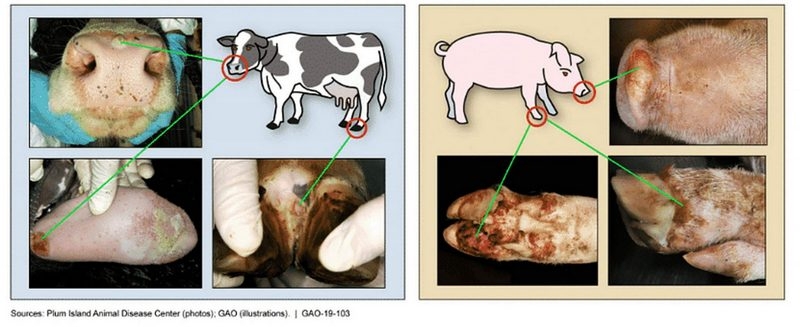
Foot-and-Mouth Disease
(1) Epidemic situation
The global foot-and-mouth disease is mainly prevalent in Africa, the Middle East, Asia and parts of South America. Among the 7 serotypes of FMDV, type O and type A are the most prevalent; Type I, II and III of South Africa are mainly prevalent in the African continent; Asian type I is mainly prevalent in the Middle East and South Asia; Type C has not been reported since its outbreak in Brazil and Kenya in 2004. In 2021, the epidemic situation of foot and mouth disease in Southeast Asia is still complex. Cambodia, Malaysia, Myanmar, Thailand, Vietnam and other countries all have outbreaks, and the strains that cause the epidemic are complex. The threat to the prevention and control of foot and mouth disease in China continues to exist.
At present, the epidemic situation of foot-and-mouth disease in China is generally stable, and foot-and-mouth disease type I in Asia remains epidemic free. There has been no foot-and-mouth disease type A epidemic in recent three years, and there will be three foot-and-mouth disease type O epidemics in 2021. According to the monitoring situation, the current FMD epidemic strains in China are still complex. Type O FMD strains include Ind-2001e, Mya-98 and CATHAY, while Type A is Sea-97. Type A A/Sea-97 overseas branch virus will be detected in border areas in 2021.
The foot-and-mouth disease vaccine in China is effective against domestic epidemic strains, and the epidemic risk points mainly exist in the links and sites with weak immunity. Based on the monitoring data, it is predicted that the FMD epidemic in China will still be dominated by FMD type O in 2022, and the simultaneous epidemic of multiple strains of FMD type O will continue, which does not rule out the possibility of spot occurrence of FMD type A; The risk of foreign strains being introduced into China still exists.
(2) Vaccine Selection
Select vaccines that match the antigenicity of local epidemic strains, and the vaccine product information can be queried in the "National Veterinary Drug Basic Information Query" platform "Veterinary Drug Product Approval Number Data" of China Veterinary Drug Information Network.
(3) Recommended Immunization Procedures
1. Scale field
The age of the first immunization of young animals was determined by taking into account factors such as maternal immunity and maternal antibody level of young animals. For example, according to the differences in immunization times of female animals and maternal antibodies, piglets can choose to be immunized at the age of 28~60 days, lambs can be immunized at the age of 28~35 days, and calves can be immunized at the age of 90 days. After the initial immunization of all newborn livestock, the booster immunization shall be carried out once every 1 month, and then every 4 to 6 months.
2. Casual care households
In spring and autumn, all susceptible domestic animals will be immunized once, and they will be compensated regularly every month. Where conditions permit, immunization can be carried out according to the immunization procedure of large-scale field.
3. Emergency Immunization
When the epidemic situation occurs, the susceptible livestock in the epidemic area and threatened area shall be given an emergency immunization. When the border area is threatened by overseas epidemic situation, combined with the risk assessment results, the susceptible livestock in the high-risk area of foot and mouth disease will be given an emergency immunization. Livestock that have been immunized within the last month may not undergo emergency immunization.
(4) Immune effect monitoring
1. Test method
The method specified in GB/T 18935-2018 Diagnostic Techniques for Foot and Mouth Disease was used for antibody detection. For those immunized with inactivated vaccine, liquid phase blocking ELISA and solid phase competitive ELISA were used to detect the immune antibody; For those immunized with synthetic peptide vaccine, VP1 structural protein ELISA was used to detect the immune antibody.
2. Immune effect evaluation
After 28 days of immunization of pigs and 21 days of immunization of other domestic animals, the antibody titer shall meet the following criteria to determine that the individual immunity is qualified:
Liquid phase blocking ELISA: antibody titer of ruminant animals such as cattle and sheep ≥ 2 ^ 7, and pig antibody titer ≥ 2 ^ 6.
Solid phase competitive ELISA: antibody titer ≥ 2 ^ 6.
vP1 structural protein antibody ELISA: positive according to the method or reagent instructions.
If the number of qualified individuals accounts for no less than 70% of the total number of immune groups, the group immunity will be determined as qualified.

Post time: Dec-19-2022
